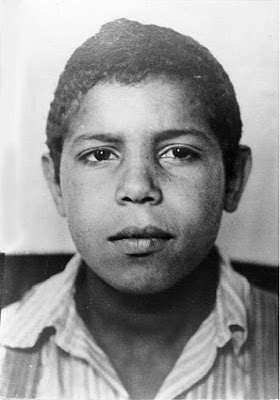
 |
| Young Rhinelander, classified as bastard and hereditarily unfit (see image description) |
the Jews during the holocaust is well known, the fate of Germany’s Black
population goes without mention. This an
interesting article on the terrible experiences of Germany’s small Black
population.
were lower on the Nazi’s racial ladder than the Jews.
 |
| African-German girl in a school photo. Pic credit: USHMM |
people know about the Nazi Holocaust, the murder of 6 million Jews and 6
million others: Russians, Gypsies, Slavs, socialists, disabled people and LGBT
people.
the big narrative of the Holocaust there are a myriad of small, individual
stories and testimonies that help illustrate and shed light on the cruelty and
barbarity of the Nazi regime.
such account is the story of what happened to Germany’s tiny black population.
Levi once wrote, “this is a story interwoven with freezing dawns”. Some
may know their story, I certainly didn’t.
away inside Hitler’s anti-Semitic diatribe, Mein Kampf, there is the
following passage:
was, and is, the Jew who brought negroes to the Rhine, brought them with the
same aim and with deliberate intent to destroy the white race he hates by
persistent bastardisation, to hurl it from the cultural and political heights
it has attained, and to ascend them as its masters.
 |
| Eugen Fischer with photographs of South African Basters, c. 1938 |
was not entirely a figment of his imagination; there were a small number of
young black children of African heritage living in the Rhineland.
most west European countries, by the 17th century, Germany had a small black
population. The modern state of Germany was founded in 1871.
number of black people living in Germany increased from 1870 onwards. They came
mainly from Germany’s small colonies in Africa and south east Asia; they were
students, artisans, entertainers, former soldiers, low-level colonial
officials, such as tax collectors, who had worked for the imperial colonial
government.
 |
| A sign saying that interaction between blacks and whites degrades the race |
population
black population of Germany at the time of the Third Reich was 20,000 – 25,000
out of a total population of over 65 million.
before the Nazis took power in 1933, Germany’s black population faced racial
discrimination and violence. Most government, religious and colonial officials
refused to register interracial marriages or births. The state promoted
eugenics, and popularised arguments about the inferiority of dual-heritage
children.
the defeat of Germany in the First World War, the Allies stripped Germany of
its colonies. Also as part of the war reparations (under the Versailles Treaty)
the Allies occupied the Rhineland in western Germany.
Carr in Germany’s Black Holocaust: 1890-1945, estimates that over
200,000 French troops occupied the Rhineland region. They included a number
black colonial troops.
Some of these African Rhineland-based soldiers married German women and raised
their children as German; other German women had children by African soldiers
outside of marriage.
vary, but there were over 800 dual-heritage children living in the Rhineland
region. The Nazis and some sections of the press labeled these children
“Rhineland Bastards” or “Rhineland Mischlingers” (mixing their blood with
“alien” races).
 |
| African-German child with his schoolmates, under the Nazi regime. Pic credit: USHMM Afro-German Hans J. Massaquoi tried to join the Nazi youth |
term “Rhineland Bastard” is of course vile. It both articulated the Nazis’
biological construction of race and colonial conceptions of race and racial
mixture that were seen as posing a threat to “white” superiority.
isolation, segregation and attempted eradication of Germany’s black population
was carried out in stages. This mirrors (obviously on a tiny scale) the methods
used by the Nazis in their attempts to wipe out Europe’s Jewish population.
 |
| Black inmate of Dachau concentration camp when liberated in 1945 |
of these children and their families fled Germany after the Nazis took power;
others were killed in the round-ups that followed.
Nazis enacted a new law providing a basis for forced sterilisation of disabled
people, Gypsies, and blacks on the 14 July 1933. If you want to read further
about this horrific practice go to Benno Muellar-Hill’s Murderous Science:
Elimination by Scientific Selection of Jews, Gypsies, and Others in Germany,
1933-1945.
the Nazis, African-German mixed-heritage children were marginalised, isolated
socially and economically, and not allowed to attend university. Racial
discrimination prohibited them from seeking most jobs.
followed the Nuremberg laws of September 1935. These prohibited miscegenation –
mixed marriages between Aryans and others. Any young Afro-German woman who got
pregnant was forced to have an abortion.
Number 3
organisation named “Commission Number 3” was created by the Nazis to deal with
the so-called problem of the “Rhineland Bastards”. This was organised under Dr
Eugen Fischer of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute of Anthropology, Human Heredity
and Eugenics. It was decided that the African-German children would be
sterilised under the 1933 Law for the Prevention of Hereditarily Diseased
Offspring.
programme began in 1937, when local officials were asked to report on all
“Rhineland Bastards” under their jurisdiction.
together, some 400 children of mixed parentage were arrested and sterilised.
The Nazis went to great lengths to conceal their sterilisation and abortion
programme.
happened to these Afro-Germans is very complex – their experiences were not
uniform. Some of these children were subjected to medical experiments and
others mysteriously “disappeared”.
Hauck, a black Holocaust survivor and a victim of Hitler’s mandatory
sterilisation programme, explained in the film Hitler’s Forgotten Victims
that when he was forced to undergo sterilisation as a teenager, he was given no
anaesthetic. Once he received his sterilisation certificate, he was “free to
go”, so long as he agreed to have no sexual relations whatsoever with Germans.
Campt, in her path-breaking book, Other Germans: Black Germans and the
Politics of Race, Gender, and Memory in the Third Reich, interviewed
several black Rhineland survivors.
published testimony from one male member of this Rhineland group. In his
complex statement he recalls being sterilised under the Nazi programme, then
later he became a member of the Hitler Youth movement. He then joined the
German army, was captured by the Russians and spent several years as a German
prisoner of war in Russia.
enough research has been done to unravel what happened to Germany’s black
population. We know that most – alongside other black Europeans and many black
soldiers – ended up in Nazi concentration camps and were murdered.
black inmate at Dachau, photographed immediately after liberation. Pic credit:
USHMM
their Jewish counterparts they did not go meekly to their deaths – they
resisted the best they could. A tiny handful survived and were able to tell
their story.
such black survivor was Johnny Voste, a Belgian resistance fighter who was arrested
in 1942 for alleged sabotage and then shipped to Dachau concentration camp.
told that one of his jobs was stacking vitamin crates in the camp. Risking his
own life, he distributed hundreds of vitamins to camp detainees, which saved
the lives of many who were starving and weak. His motto was: “No, you can’t
have my life; I will fight for it.”
Obit of the Day: “Growing Up Black in Nazi Germany”
http://www.obitoftheday.com/post/41275233204/hansmassaquoi
Hans Massaquoi was very disappointed when his teacher told him that he could
not join the Hitler Youth. Massaquoi’s friends had all joined and he was
enthralled with the uniforms, the parades, the camp-outs. But Hans’ desire to
join was trumped by the color of his skin.
Born in 1926, Mr. Massaquoi’s parents were a German nurse and the son of a
Liberian diplomat. He would grow up in Hamburg as the Weimar Republic was
collapsing and the the Third Reich was building up.
When he was in second grade, Mr. Massaquoi was so taken with the Nazi
imagery that, at his request, his nanny sewed a swastika to his sweater.
Although his mother removed it when he returned home from school, a picture had
already been taken. (See above.)
Mr. Massaquoi’s family lived in Germany for the duration of the war.
According to Mr. Massaquoi’s memoir, Destined to Witness,
he theorized that there were so few blacks living in Germany that they were a
low priority for extermination. Eventually he would move: first to his father’s
home country of Liberia and later to Chicago.
In the United States, although trained in aviation mechanics, Mr. Massaquoi
would become a writer for Jet magazine and eventual move to its sister
publication, Ebony, where he became managing editor.
Mr. Massaquoi, who passed away on January 19, 2013 on his 87th birthday, was
encouraged to write down the story of his unusual childhood by his friend and
author of Roots, Alex Haley.
Sources: L.A.
Times and Chicago
Sun-Times
(Image is from Mr. Massaqoui’s collection and copyright of William Morrow
Paperbacks via spiritosanto.wordpress.com)